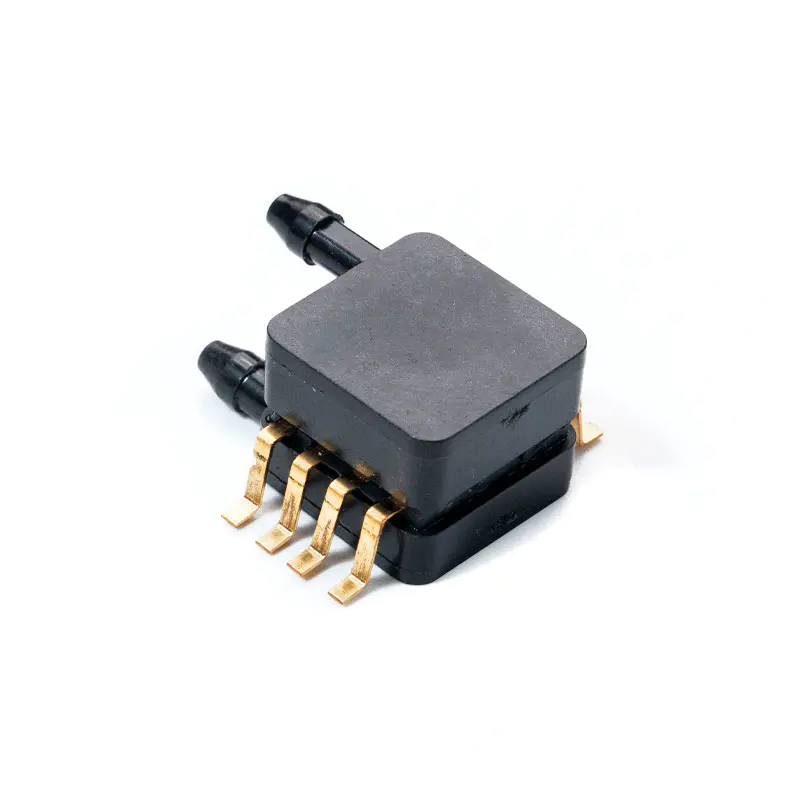
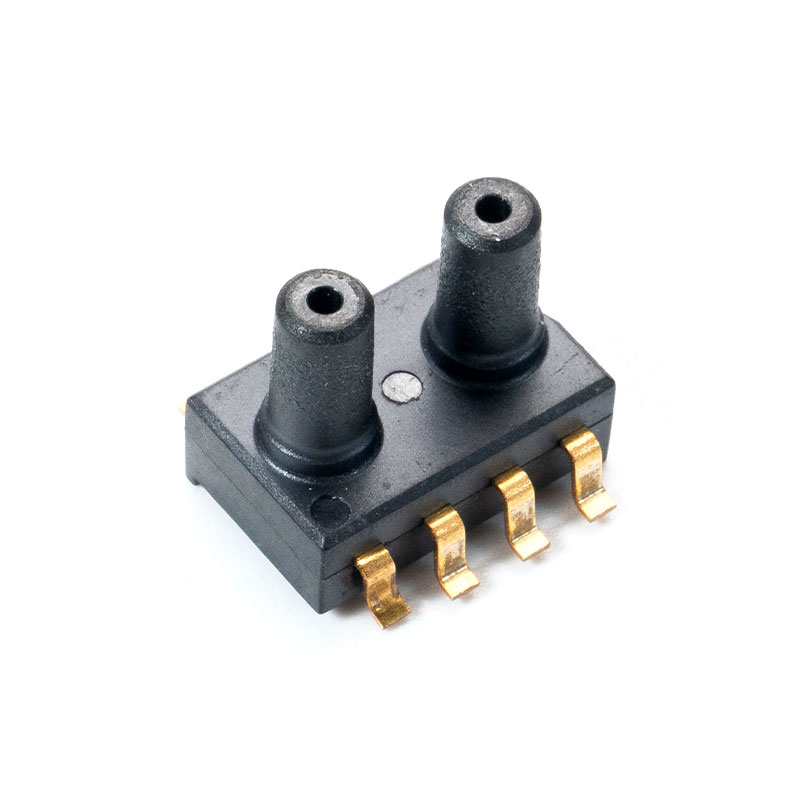
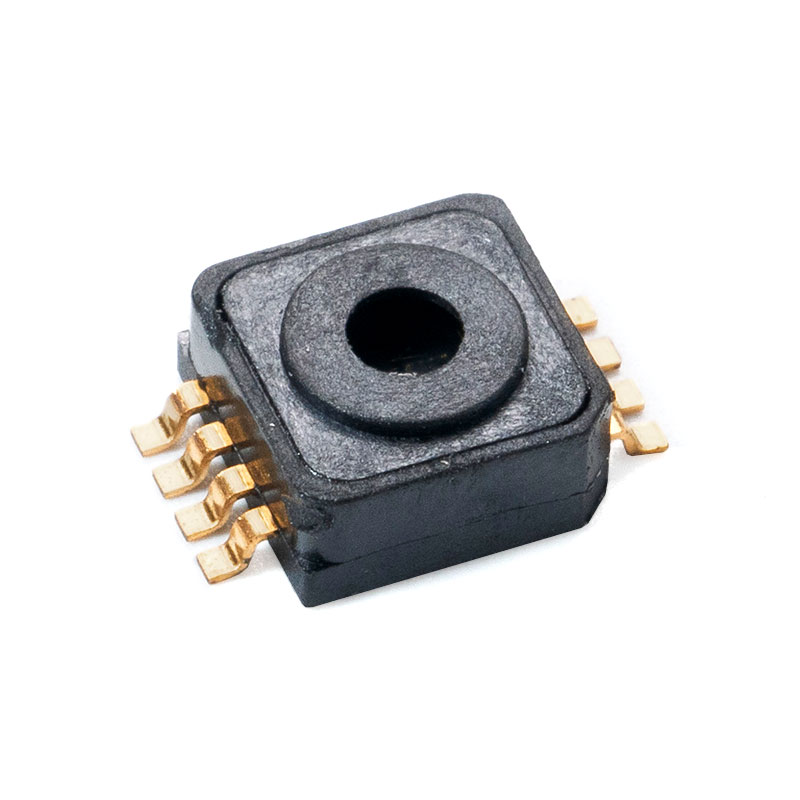
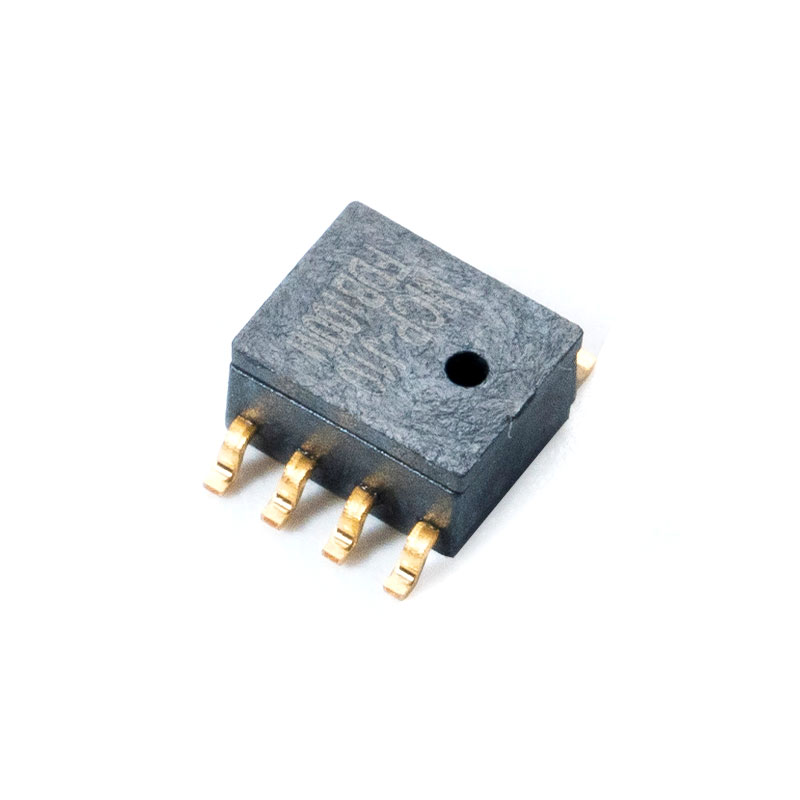
What Makes a Pressure Sensor Reliable?
Date:2025-12-24
- 1 Understanding Micro Pressure Sensor Technologies
- 2 The Role of Low Pressure Sensor in HVAC and Fluid Systems
- 3 How Medium Pressure Sensor Supports Industrial Automation
- 4 Technical Comparison of Micro, Low, and Medium Pressure Sensors
- 5 Integration Best Practices
- 6 FAQ
- 6.1 What is the difference between micro, low, and medium pressure sensors?
- 6.2 Can micro pressure sensors be used in medical devices?
- 6.3 Why are water-resistant low pressure sensors important?
- 6.4 How do medium pressure sensors integrate with industrial systems?
- 6.5 What factors affect sensor accuracy?
Understanding Micro Pressure Sensor Technologies
In high-precision measurement systems, Micro Pressure Sensor devices play a critical role. Designed to detect minute pressure changes, these sensors are widely used in medical, environmental, and industrial applications. For example, a micro pressure sensor for medical devices provides accurate readings in ventilators, infusion pumps, and patient monitoring systems. Modern digital designs, such as the digital micro pressure sensor with high accuracy, integrate advanced MEMS technology to deliver stable outputs and low drift under varying environmental conditions.
- Compact MEMS design enables integration into small devices
- High-resolution digital output supports microcontroller interfacing
- Temperature and humidity compensation ensures reliable performance
- Applications include medical, environmental, and lab instrumentation
The Role of Low Pressure Sensor in HVAC and Fluid Systems
Low pressure sensors are essential for monitoring airflows, fluid systems, and HVAC operations. The low pressure sensor for HVAC systems accurately tracks duct pressures, ensuring efficient ventilation. Additionally, the water-resistant low pressure sensor for fluid monitoring protects against moisture and liquid exposure while maintaining precision. Selecting the right sensor requires understanding pressure range, environmental exposure, and signal interface.
- Ensures HVAC system balance and energy efficiency
- Monitors filters, airflow, and pump operations
- Resistant to moisture and condensation for fluid monitoring
- Enables predictive maintenance and system diagnostics
| Sensor Type | Pressure Range | Typical Application |
| Micro | 0–500 Pa | Medical devices, lab instruments |
| Low | 0–50 kPa | HVAC, fluid monitoring |
| Medium | 50 kPa–2 MPa | Industrial automation, machinery |
How Medium Pressure Sensor Supports Industrial Automation
The medium pressure sensor for industrial automation is designed to handle higher load pressures while maintaining accuracy. These sensors are integral in robotic systems, CNC machinery, and hydraulic equipment, where consistent readings prevent mechanical failures. Advanced MEMS designs also allow integration with digital controllers, providing real-time monitoring and fault detection.
- Handles higher pressure ranges without sacrificing accuracy
- Compatible with industrial automation protocols
- Reduces downtime via predictive maintenance
- Supports digital output interfaces for PLC and microcontroller systems
Technical Comparison of Micro, Low, and Medium Pressure Sensors
Choosing the right pressure sensor depends on multiple performance factors including range, sensitivity, environmental stability, and output interface. Below is a comparative matrix illustrating differences across sensor types:
| Feature | Micro Pressure Sensor | Low Pressure Sensor | Medium Pressure Sensor |
| Typical Pressure Range | 0–500 Pa | 0–50 kPa | 50 kPa–2 MPa |
| Application | Medical, lab devices | HVAC, fluid systems | Industrial automation |
| Output Type | Digital (I²C/SPI) | Analog/Digital | Analog/Digital |
| Environmental Resistance | Moderate | High (water-resistant) | High |
| Accuracy | High | Medium–High | High |
Integration Best Practices
To maximize performance, sensors must be calibrated correctly and mounted according to environmental conditions. For micro pressure sensors, avoid high-vibration areas. Low pressure sensors require protection against moisture ingress. Medium pressure sensors should integrate with digital controllers to enable real-time monitoring.
- Ensure proper calibration for each application
- Use protective housing for moisture-sensitive environments
- Consider digital outputs for automated systems
- Regularly verify sensor readings for quality control
FAQ
What is the difference between micro, low, and medium pressure sensors?
Micro pressure sensors detect very small pressure changes (0–500 Pa) and are used in medical and laboratory equipment. Low pressure sensors (0–50 kPa) monitor HVAC systems and fluid applications. Medium pressure sensors (50 kPa–2 MPa) are ideal for industrial automation and machinery monitoring. Choosing depends on pressure range, environmental conditions, and required accuracy.
Can micro pressure sensors be used in medical devices?
Yes. The micro pressure sensor for medical devices is widely used in ventilators, infusion pumps, and patient monitoring systems due to its high accuracy, compact size, and reliable digital output.
Why are water-resistant low pressure sensors important?
Water-resistant low pressure sensors, such as the water-resistant low pressure sensor for fluid monitoring, prevent damage from moisture or liquid exposure while maintaining precise measurements, critical in HVAC and fluid system monitoring.
How do medium pressure sensors integrate with industrial systems?
The medium pressure sensor for industrial automation can interface with PLCs and microcontrollers using analog or digital outputs. This enables real-time monitoring, fault detection, and predictive maintenance in complex industrial workflows.
What factors affect sensor accuracy?
Accuracy depends on sensor type, pressure range, environmental conditions, calibration, and output interface. Digital micro sensors with high accuracy, such as the digital micro pressure sensor with high accuracy, use MEMS technology and temperature compensation to ensure stable readings under varying conditions.

Recommended Articles


 English
English Français
Français 中文简体
中文简体